Building an Upgradable Contract Using Transparent Proxy Pattern
Setting up your project
Create a new directory for your project and navigate to it:
mkdir jumbochain-upgradable-contracts
cd jumbochain-upgradable-contracts
Install hardhat globally with:
npm install --global hardhat
Initialize hardhat project with
npx hardhat init
Choose empty config option like following:
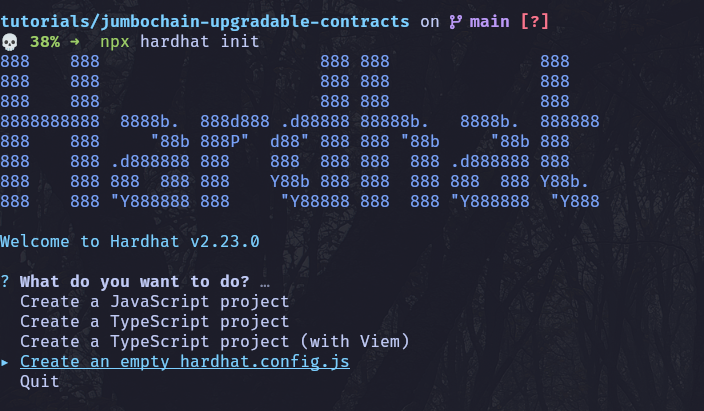
Install dependency prompted by tool, for my case it was:
npm install --save-dev "hardhat@^2.23.0"
Install dependencies that we are going to need in upcoming task:
npm install @openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable
npm install --save-dev @openzeppelin/hardhat-upgrades @nomicfoundation/hardhat-ethers @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox
npm install dotenv ethers
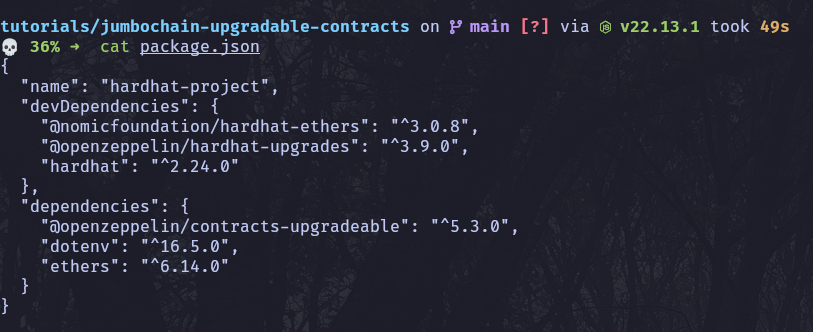
After this your package.json should look similar to this:
Create .env to manage variables
touch .env
Add this variables to the file (use your own private key and rpc url accordingly):
RPC_URL=https://testnode.jumbochain.org is protojumbo testnet url.
Also you can use metamask to create wallet on testnet and retrieve private key to use here.
RPC_URL="https://testnode.jumbochain.org"
OWNER_KEY="2a3569dbc2f6afb8ad94eb65ac23d8530538b3ed153d8dfae26e163c80fcbbad"
Configure Hardhat
Now lets modify hardhat.config.js to include the network configuration for Jumbo Blockchain:
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
require("@openzeppelin/hardhat-upgrades");
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-ethers");
require("dotenv").config();
/** @type import('hardhat/config').HardhatUserConfig */
module.exports = {
solidity: {
compilers: [
{
version: "0.8.20"
}
]
},
networks: {
hardhat: {},
jumbochain: {
url: process.env.RPC_URL || "https://testnode.jumbochain.org",
accounts: [`${process.env.OWNER_KEY}`],
}
}
};
Writing upgradeable contracts
Initial contract
Lets create the first version of the contract ContractV1.sol in contracts directory.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
// Upgradeable contract ke liye initializer use karte hain
import "@openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable/proxy/utils/Initializable.sol";
contract ContractV1 is Initializable {
uint256 public storedNumber;
function initialize() public initializer {
storedNumber = 42; // Set a default value
}
function setStoredNumber(uint256 _newNumber) public {
storedNumber = _newNumber;
}
function getStoredNumber() public view returns (uint256) {
return storedNumber;
}
}
Deploying the initial implementation
Create a deployment script (scripts/deployV1.js) for the deployment as follows.
const { ethers, upgrades } = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const contractV1 = await ethers.getContractFactory("ContractV1");
console.log("Deploying MyContractV1...");
const proxy = await upgrades.deployProxy(contractV1, []);
await proxy.waitForDeployment();
console.log("contractV1 Proxy deployed to", await proxy.getAddress());
}
main();
Run the deployment script using:
npx hardhat run scripts/deployV1.js --network jumbochain
After deployment output should look similar to this:
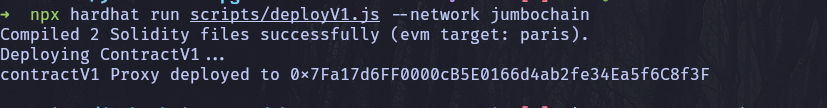
Now lets pick up the contract address and add to the .env file, we will use it
in next steps.
Now .env should look similar to this.
➜ cat .env
RPC_URL="https://testnode.jumbochain.org"
OWNER_KEY="2a3569dbc2f6afb8ad94eb65ac23d8530538b3ed153d8dfae26e163c80fcbbad"
CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS="0x7Fa17d6FF0000cB5E0166d4ab2fe34Ea5f6C8f3F"
Upgraded version
Next, create the second version of the contract ContractV2.sol that
extends ContractV1 and introduces new functionality:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable/proxy/utils/Initializable.sol";
import "./ContractV1.sol";
contract ContractV2 is ContractV1 {
function doubleStoredNumber() public {
storedNumber = storedNumber * 2;
}
}
Initial contract (ContractV1) is already deployed, now we will upgrade it using the script.
Deploy upgrade
Create an upgrade script (scripts/deployV2.js):
const { ethers, upgrades } = require("hardhat");
const CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS = process.env.CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS;
async function main() {
const contractV2 = await ethers.getContractFactory("ContractV2");
console.log("Upgrading to ContractV2...");
const upgraded = await upgrades.upgradeProxy(CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS, contractV2);
await upgraded.waitForDeployment();
console.log("Upgrade done. ContractV2 deployed to: ", await upgraded.getAddress());
}
main();
Run the upgrade with:
npx hardhat run scripts/deployV2.js --network jumbochain
Output should look similar to this:
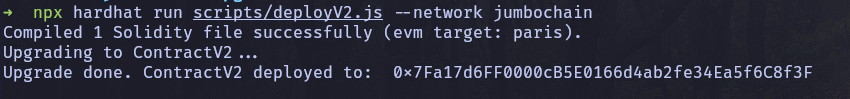
As you can observe, both the initial deployed address and address after the upgrade are the same
With next steps we will verify the if the functionality of V1 and upgrade V2 both are working on deployed contract.
Interacting with the Contract
To interact with the deployed contract, use simple scripts for reading and writing data.
Use ContractV1 functionality
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
require("dotenv").config();
async function main() {
const CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS = process.env.CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS;
if (!CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS) {
throw new Error("Please set CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS in your .env file");
}
const contractV1 = await ethers.getContractFactory("ContractV1");
const contract = contractV1.attach(CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS);
const newValue = 99; // You can change this value to any number
const tx = await contract.setStoredNumber(newValue);
await tx.wait();
console.log(`Stored number successfully set to: ${newValue}`);
}
main().catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
process.exit(1);
});
Run the script with:
npx hardhat run scripts/setStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Output should look like this:
➜ npx hardhat run scripts/setStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Stored number successfully set to: 99
Verify we have correctly used setStoredNumber functionality by fetching the
stored number value from contract.
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
require("dotenv").config();
async function main() {
const CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS = process.env.CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS;
if (!CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS) {
throw new Error("Please set CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS in your .env file.");
}
const contractV1 = await ethers.getContractFactory("ContractV1");
const contract = contractV1.attach(CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS);
const storedNumber = await contract.getStoredNumber();
console.log("Stored number is:", storedNumber.toString());
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
Run the script with:
npx hardhat run scripts/getStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Output should look similar following and with this we have confirmed that
initial deployed ContractV1 functionality.
➜ npx hardhat run scripts/getStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Stored number is: 99
Use upgraded functionality added by ContractV2
Doubling the Stored Number:
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
require("dotenv").config();
async function main() {
const CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS = process.env.CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS;
if (!CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS) {
throw new Error("Please set CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS in your .env file");
}
const contractV2 = await ethers.getContractFactory("ContractV2");
const contract = contractV2.attach(CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS);
const tx = await contract.doubleStoredNumber();
await tx.wait();
console.log("Stored number doubled successfully.");
}
main().catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
process.exit(1);
});
Run the script with:
npx hardhat run scripts/doubleStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Should output this:
➜ npx hardhat run scripts/doubleStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Stored number doubled successfully.
Now run getStoredNumber.js again to verify the new value is doubled:
npx hardhat run scripts/getStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Output should look like this:
➜ npx hardhat run scripts/getStoredNumber.js --network jumbochain
Stored number is: 198
Notice when using upgraded functionality the contract address remains same as
of the initially deployed contract i.e. CONTRACT_V1_ADDRESS.
Thus we have successfully upgraded our contract using Transparent Proxy Pattern